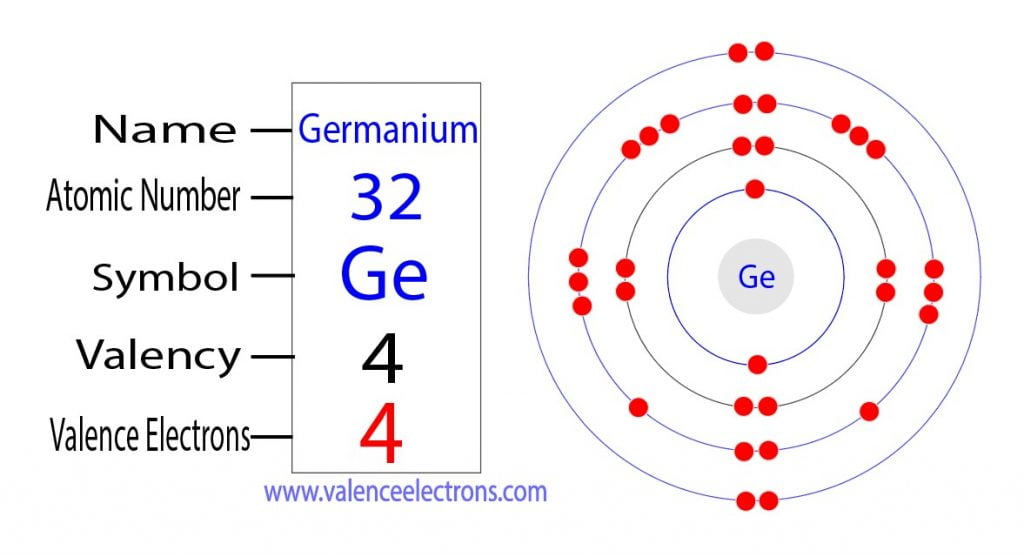
How to Find the Valence Electrons for Germanium (Ge)?
Germanium Ion After Ge ion irradiation, the XRD spectrum was typical of an amorphous phase and the electrical resistivity value was comparable to that measured in the as deposited amorphous film. From: Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2021 Related terms: Energy Engineering Nanoparticle Germanium Laser Excitation Aqueous Solution
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-685028985-5bb389d946e0fb00261ea558.jpg)
Germanium Facts (Atomic Number 32 or Ge)
It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements.
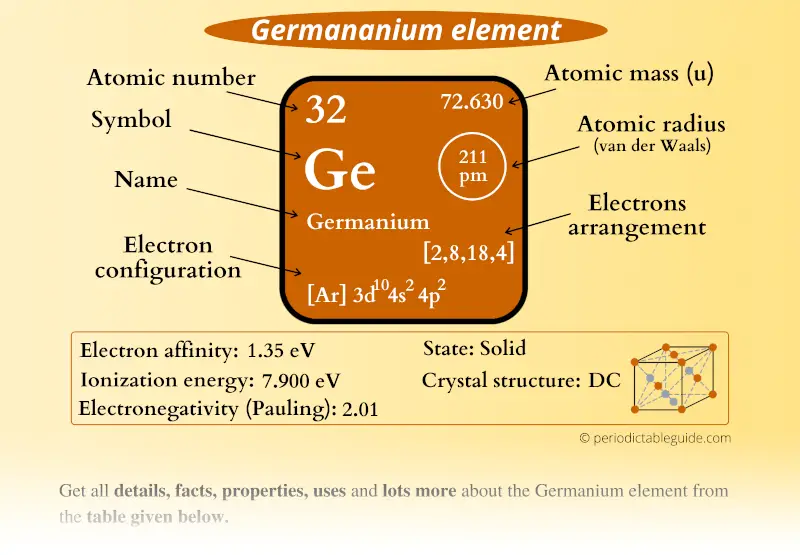
Germanium Element Periodic table What type of element is it?
Germanium does not appear in commercial quantities as a native ore but is produced principally as a by-product of zinc processing, with a smaller amount from the processing of copper. The germanium-containing metallic zinc is first distilled under nonoxidizing conditions.. 22.1.2 Ion exchange. Precipitation. Dowex-50 cation-exchanger retains.

Germanium Electron Affinity Electronegativity Ionization Energy
The primary sources of worldwide germanium production are Zn-refinery residue and coal fly ash, with recycling of industrial scraps being the secondary source [12].Globally, the main producer of germanium is China, accounting for 80% of world production during 2012-2016 [7].Other producers are Russia, Finland, US, Japan, and Ukraine, with Finland accounting for 10%, Russia for 5% (primarily.

Germanium Periodic Table and Atomic Properties
Germanium (Ge) ion implantation into silicon waveguides will induce lattice defects in the silicon, which can eventually change the crystal silicon into amorphous silicon and increase the refractive index from 3.48 to 3.96.
Element of Germanium stock vector. Illustration of atom 104400449
Germanium Ion From: Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2022 Process Simulation: Kinetic Monte Carlo I. Martin-Bragado, M. Jaraiz, in Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering, 2016 2.1 Si: Amorphization and Recrystallization

Germanium, atomic structure Stock Image C023/2522 Science Photo
Abstract In recent decade, special interest is paid to germanium as potential material of negative electrodes in lithium-ion and, the more so, sodium-ion batteries. In the review, studies of lithium and sodium reversible insertion to different germanium-metal nanostructures as well as germanium-alloy-, germanium-compound-, and germanium-composite-based electrodes are overviewed. The.

Germanium Facts, Symbol, Discovery, Properties, Uses
Germanium - Ionization Energy. First Ionization Energy of Germanium is 7.9 eV. Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the energy necessary to remove an electron from the neutral atom. Skip to content Menu Periodic Tables All Properties Atomic Numbers Atomic Masses Atomic Radii Densities Electron Configurations Electron Affinities

Chemist Atom of Germanium Diagram Stock Vector Illustration of
Germanium, a promising electrode material for high-capacity lithium ion batteries (LIBs) anodes, attracted much attention because of its large capacity and remarkably fast charge/discharge kinetics.

Germanium chemical element periodic table science symbol Stock Photo
Chemistry in its element: germanium For a good fifty years, germanium was little more than a box on the periodic table. It really wasn't good for anything. It was only with the development of electronics that germanium's value as a very effective semiconductor came to light.
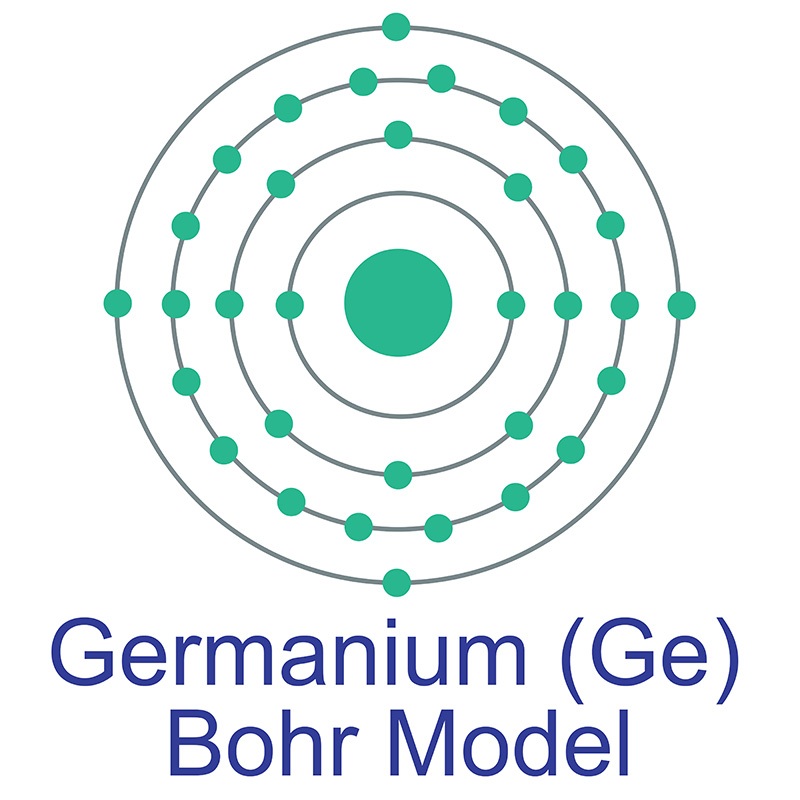
Germanium (Ge) AMERICAN ELEMENTS
Germanium is stable in air and water, and is unaffected by alkalis and acids, except nitric acid. Applications. Germanium is an important semiconductor, mainly used in transistors and integrated circuits. They are often made from germanium to which small amounts of arsenic, gallium, or other metals. Germanium forms many compounds.
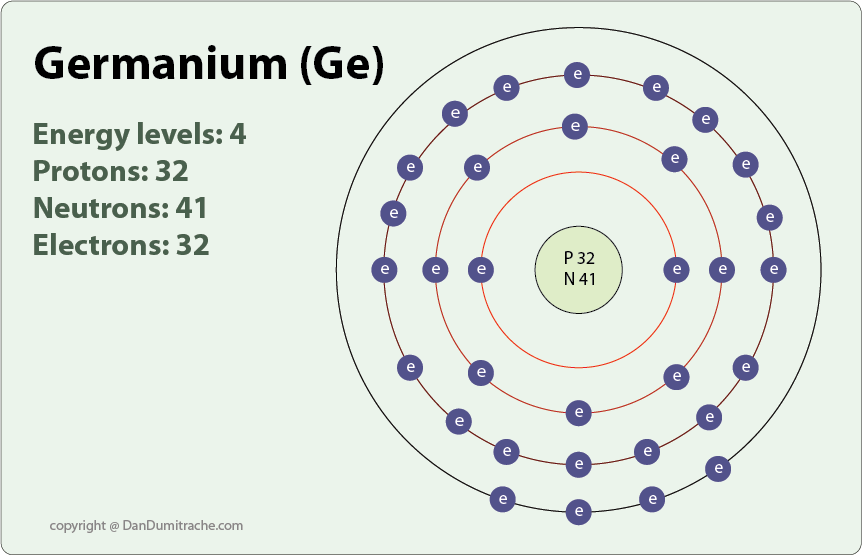
What is the atomic structure of germanium? Socratic
Ionic radius (1+ ion) - Ionic radius (2+ ion) 87 pm : Ionic radius (3+ ion) - Ionic radius (1- ion) - Ionic radius (2- ion) -. Electrical conductivity : 3 S m-1: Freezing/Melting point: 938 o C, 1210.6 K : Discovery of Germanium. Dr. Doug Stewart. Germanium was one of the elements whose existence was predicted in 1869 by Russian.

Electron Configuration for Germanium (Ge, Ge2+, Ge4+ ions)
In chemistry, germanate is a compound containing an oxyanion of germanium. In the naming of inorganic compounds it is a suffix that indicates a polyatomic anion with a central germanium atom, [1] for example potassium hexafluorogermanate, K 2 GeF 6. [2] Germanium is similar to silicon forming many compounds with tetrahedral {GeO 4 } [2] units.

Germanium Chemical Element Photograph by Science Picture Co
germanium (Ge), a chemical element between silicon and tin in Group 14 (IVa) of the periodic table, a silvery-gray metalloid, intermediate in properties between the metals and the nonmetals.

Symbol and electron diagram for Germanium illustration Stock Vector
Germanium is mainly a byproduct of zinc ore processing. It is a hard, grayish-white element; it has a metallic luster and the same crystal structure as diamond; and it is brittle, like glass.In addition, it is important to note that germanium is a semiconductor, with electrical properties between those of a metal and an insulator. The development of the germanium transistor opened the door to.
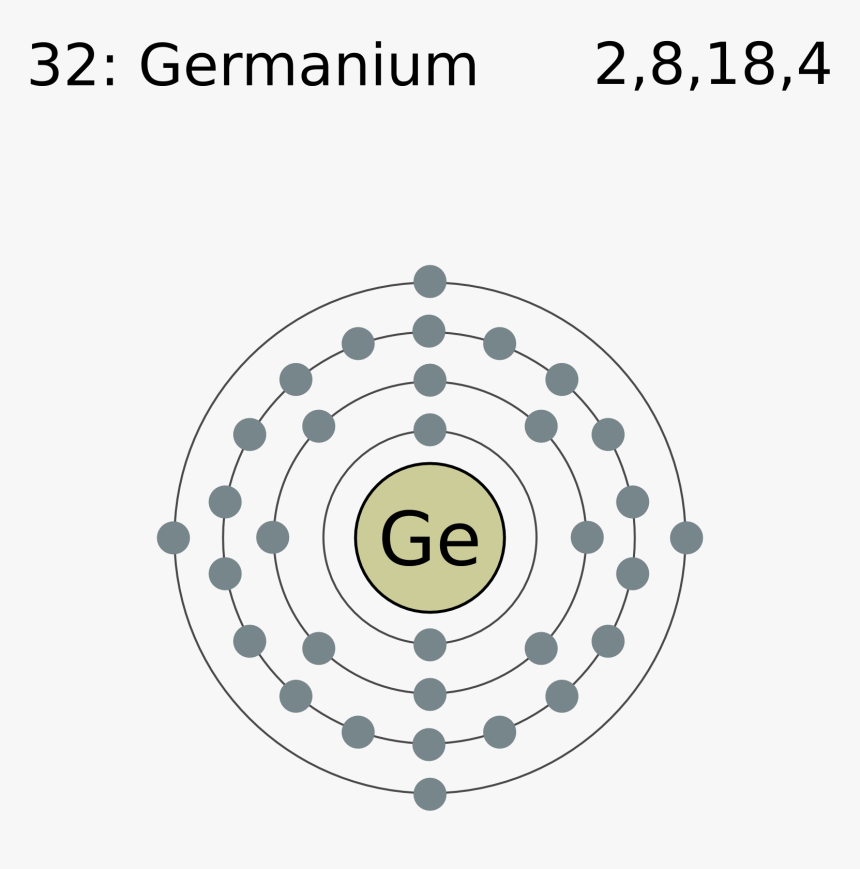
Electron Shell 032 Germanium Germanium Valence Electrons, HD Png
This great but unpredictable progress was fertilized by three basic parameters: the continuous development of new and efficient laser sources and processing methods, the deeper understanding of the underlying laser-matter interactions, and the evolution of the optical fiber from a simple optical cable to a versatile and efficient photonic device.